Hash table implementation with separate chaining. More...
#include <hashTable.h>
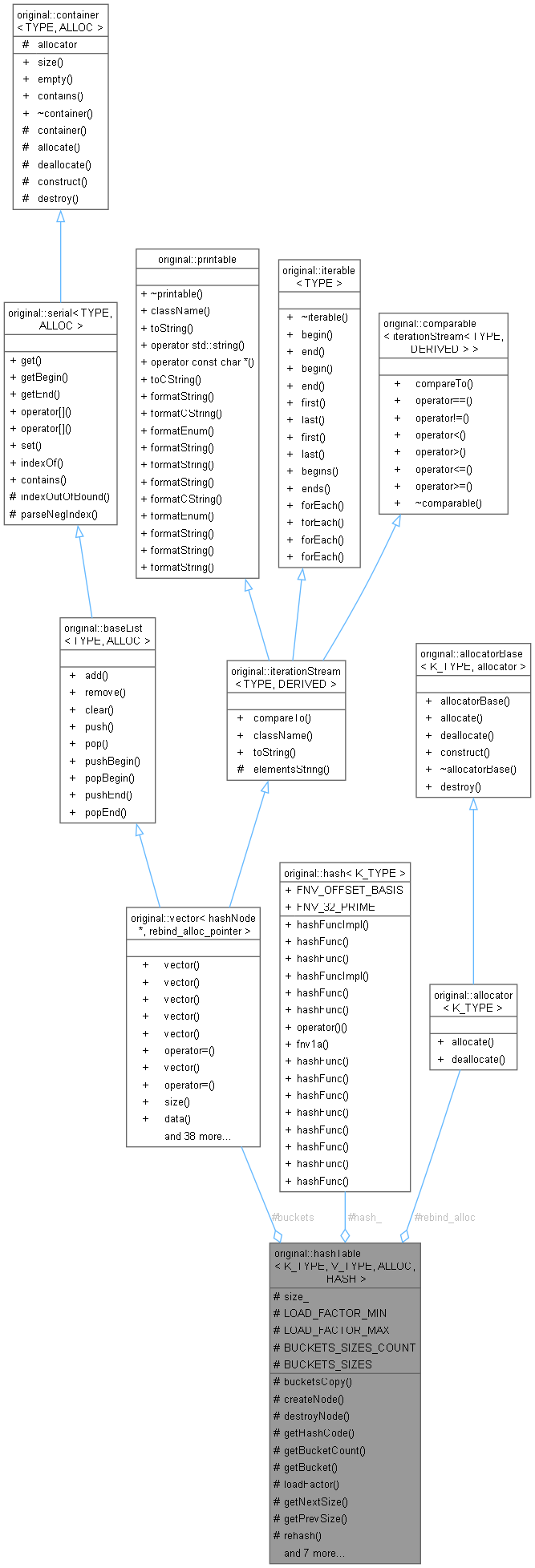
Classes | |
| class | hashNode |
| Internal node type for hash table storage. More... | |
| class | Iterator |
| Forward iterator for hashTable. More... | |
Protected Types | |
| using | rebind_alloc_node = typename ALLOC::template rebind_alloc<hashNode> |
| Rebound allocator type for node storage. | |
| using | rebind_alloc_pointer = typename ALLOC::template rebind_alloc<hashNode*> |
| Rebound allocator type for pointer storage. | |
| using | buckets_type = vector<hashNode*, rebind_alloc_pointer> |
| Type representing the hash table buckets container. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| buckets_type | bucketsCopy (const buckets_type &old_buckets) const |
| Creates a deep copy of the hash table's bucket array. | |
| hashNode * | createNode (const K_TYPE &key=K_TYPE{}, const V_TYPE &value=V_TYPE{}, hashNode *next=nullptr) const |
| Creates a new hash node. | |
| void | destroyNode (hashNode *node) noexcept |
| Destroys a hash node. | |
| u_integer | getHashCode (const K_TYPE &key) const |
| Computes hash code for a key. | |
| u_integer | getBucketCount () const |
| Gets current number of buckets. | |
| hashNode * | getBucket (const K_TYPE &key) const |
| Gets bucket head for a key. | |
| floating | loadFactor () const |
| Calculates current load factor. | |
| u_integer | getNextSize () const |
| Gets next appropriate bucket size for expansion. | |
| u_integer | getPrevSize () const |
| Gets previous appropriate bucket size for shrinking. | |
| void | rehash (u_integer new_bucket_count) |
| Rehashes table to new bucket count. | |
| void | adjust () |
| Adjusts table size based on load factor. | |
| hashTable (HASH hash=HASH{}) | |
| Constructs empty hashTable. | |
| hashNode * | find (const K_TYPE &key) const |
| Finds node for given key. | |
| bool | modify (const K_TYPE &key, const V_TYPE &value) |
| Modifies value for existing key. | |
| bool | insert (const K_TYPE &key, const V_TYPE &value) |
| Inserts new key-value pair. | |
| bool | erase (const K_TYPE &key) |
| Removes key-value pair. | |
| ~hashTable () | |
| Destroys hashTable. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| u_integer | size_ |
| buckets_type | buckets |
| HASH | hash_ |
| rebind_alloc_node | rebind_alloc {} |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| static constexpr floating | LOAD_FACTOR_MIN = 0.25 |
| Minimum load factor before shrinking. | |
| static constexpr floating | LOAD_FACTOR_MAX = 0.75 |
| Maximum load factor before expanding. | |
| static constexpr u_integer | BUCKETS_SIZES_COUNT = 30 |
| Size of BUCKETS_SIZES BUCKETS_SIZES. | |
| static constexpr u_integer | BUCKETS_SIZES [] |
| Predefined bucket sizes for hash table resizing. | |
Detailed Description
class original::hashTable< K_TYPE, V_TYPE, ALLOC, HASH >
Hash table implementation with separate chaining.
- Template Parameters
-
K_TYPE Key type (must be hashable) V_TYPE Value type ALLOC Allocator type (default: allocator<K_TYPE>) HASH Hash function type (default: hash<K_TYPE>)
This class provides a generic hash table implementation that serves as the base for hash-based containers. It implements:
- Key-value pair storage
- Dynamic resizing
- Basic hash table operations
Performance Characteristics:
- Insertion: Average O(1), Worst O(n)
- Lookup: Average O(1), Worst O(n)
- Deletion: Average O(1), Worst O(n)
The implementation guarantees:
- Unique keys (no duplicates)
- Automatic resizing when load factor thresholds are crossed
- Exception safety (basic guarantee)
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ hashTable()
|
explicitprotected |
Constructs empty hashTable.
- Parameters
-
hash Hash function to use
◆ ~hashTable()
|
protected |
Destroys hashTable.
Cleans up all nodes and buckets
Member Function Documentation
◆ adjust()
|
protected |
Adjusts table size based on load factor.
Checks current load factor and resizes if:
- loadFactor() >= LOAD_FACTOR_MAX: expands table
- loadFactor() <= LOAD_FACTOR_MIN: shrinks table
◆ bucketsCopy()
|
protected |
Creates a deep copy of the hash table's bucket array.
- Parameters
-
old_buckets The original old_buckets array to copy
- Returns
- A new old_buckets array with cloned nodes
This function performs a deep copy of the entire old_buckets array used by the hash table, including the internal linked list in each bucket (used for separate chaining).
Copying strategy:
- For each bucket index, traverse the linked list of hash nodes
- Use
createNode()to allocate a new node for each entry - Preserve the order of elements within each bucket's chain
This method is typically used in:
- Copy constructors
- Copy assignment operators
The function ensures that:
- The original and copied hash tables do not share memory
- All keys and values are copied correctly
- Iterator validity is preserved for the new structure
- Note
- This function assumes the original old_buckets are well-formed (no cycles).
- Uses allocator rebound to allocate memory for the new nodes.
◆ createNode()
|
protected |
Creates a new hash node.
- Parameters
-
key Key for new node value Value for new node next Next node in chain
- Returns
- Pointer to newly created node
- Note
- Uses the rebound allocator for memory management
◆ destroyNode()
|
protectednoexcept |
Destroys a hash node.
- Parameters
-
node Node to destroy
- Note
- Safely handles nullptr and uses rebound allocator
◆ erase()
|
protected |
Removes key-value pair.
- Parameters
-
key Key to remove
- Returns
- true if key existed and was removed
- Note
- Automatically adjusts table size if needed
◆ find()
|
protected |
Finds node for given key.
- Parameters
-
key Key to search for
- Returns
- Pointer to node if found, nullptr otherwise
◆ getBucket()
|
protected |
Gets bucket head for a key.
- Parameters
-
key Key to lookup
- Returns
- Pointer to first node in bucket's chain
◆ getBucketCount()
|
protected |
Gets current number of buckets.
- Returns
- Current bucket count
◆ getHashCode()
|
protected |
Computes hash code for a key.
- Parameters
-
key Key to hash
- Returns
- Computed bucket index
◆ getNextSize()
|
protected |
Gets next appropriate bucket size for expansion.
- Returns
- Next larger bucket size from predefined primes
- Exceptions
-
outOfBoundError if already at maximum size
◆ getPrevSize()
|
protected |
Gets previous appropriate bucket size for shrinking.
- Returns
- Next smaller bucket size from predefined primes
◆ insert()
|
protected |
Inserts new key-value pair.
- Parameters
-
key Key to insert value Value to associate
- Returns
- true if inserted, false if key already existed
- Note
- Automatically adjusts table size if needed
◆ loadFactor()
|
protected |
Calculates current load factor.
- Returns
- Current elements/buckets ratio
◆ modify()
|
protected |
Modifies value for existing key.
- Parameters
-
key Key to modify value New value
- Returns
- true if key existed and was modified
◆ rehash()
|
protected |
Rehashes table to new bucket count.
- Parameters
-
new_bucket_count New number of buckets
Rebuilds the hash table with new bucket count:
- Allocates new buckets vector
- Rehashes all elements
- Maintains element order within buckets
- Note
- Invalidates all iterators
Member Data Documentation
◆ BUCKETS_SIZES
|
staticconstexprprotected |
Predefined bucket sizes for hash table resizing.
An array of prime numbers carefully selected for hash table bucket sizes. These primes are used during table resizing to maintain optimal performance characteristics.
Key Properties:
- All values are prime numbers to reduce hash collisions
- Each size is approximately double the previous (with some variance)
- Covers a wide range from small to very large tables
- Specifically chosen to avoid common modulo patterns
Selection Criteria:
- Primes spaced roughly exponentially (growth factor ~1.8-2.2)
- Avoid primes close to powers of 2 to prevent clustering
- Sufficient gaps between sizes to justify resize operations
- Includes sizes suitable for both small and large datasets
Performance Impact:
- Larger sizes reduce collisions but increase memory usage
- Smaller sizes conserve memory but may increase collisions
- The growth factor balances between resize frequency and memory overhead
The sequence continues until reaching sizes suitable for maximum practical in-memory hash tables (over 100 million buckets).
- Note
- The actual resize operation only occurs when the load factor exceeds thresholds, not necessarily at every size transition.
- See also
- LOAD_FACTOR_MIN
- LOAD_FACTOR_MAX
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- src/core/hashTable.h
Generated by